NG Tube Feeding
Resources
What is a Feeding Tube?
A feeding tube is a medical device used to provide nutrition to people who cannot take food through their mouth (orally), are unable to swallow safely or cannot take in enough calories orally, so may need additional supplementary nutrition.
Different Types Of Feeding Tubes:
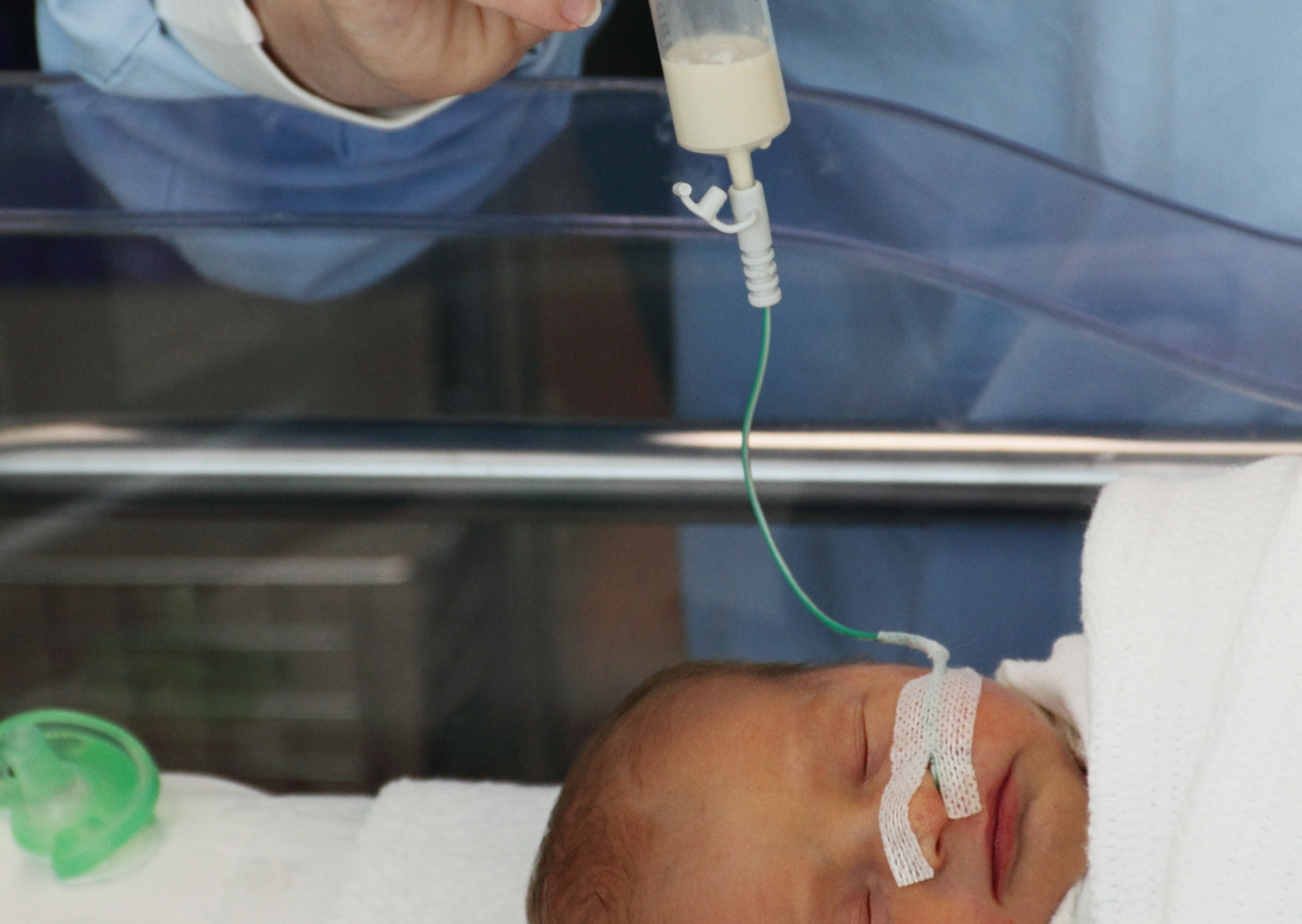
Nasogastric (NG) Tube
Nasogastric (NG) or Nasojejunal Tube (NJ) – This is a tube that goes down the nose (Nasal) and either into the stomach (Gastric) or small intestine (Jejunum). These tubes are placed relatively easily at bedside in the hospital, however the doctor may send you for an X-Ray after it has been placed to confirm that it is in fact in your stomach or small intestine and not in your lungs. Generally the nurses will do a litmus test to confirm placement too. This is where they will draw some of your stomach contents out of the tube and put it onto a piece of litmus paper to determine the acidity of what they have taken out.
If the tube is in your stomach, the stomach acid will turn the litmus paper a different colour. If you are discharged with an NG tube, you may need to ask for litmus paper as it is recommended to confirm placement daily as an NG tube can move into your lungs which can be very dangerous. It is for this reason that generally you will not be discharged with an NG or NJ tube. The usual length of time that you would keep an NG tube in would be for about 4-6 Weeks. Long term use may cause damage to the lining in the nose and back of the throat, so in cases where patients are not expected to eat for a long time the doctors would rather recommend inserting a PEG.
The doctor would usually recommend an NG tube first, however in certain instances feeding into the stomach is not feasible or possible and then they would opt for an NJ. These are cases where the stomach does not work for medical reasons or even in cases with severe vomiting and reflux.